Green Space Detection
CITY is using Deep Learning Tools for monitoring and assessing urban forest cover and to provide basic reference data for ecosystem services such as air purification and carbon sequestration.
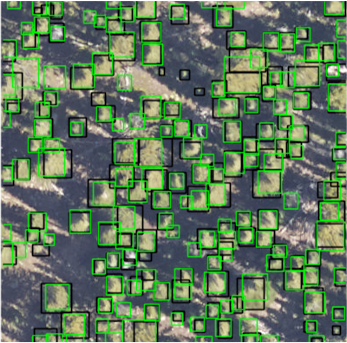
The intended output is the use of remote sensing and deep learning architecture to build a tool to estimate the tree cover area through pixel classification. We formulate a multi-spectral classifier for tree cover estimation. This dataset is to be made publicly available
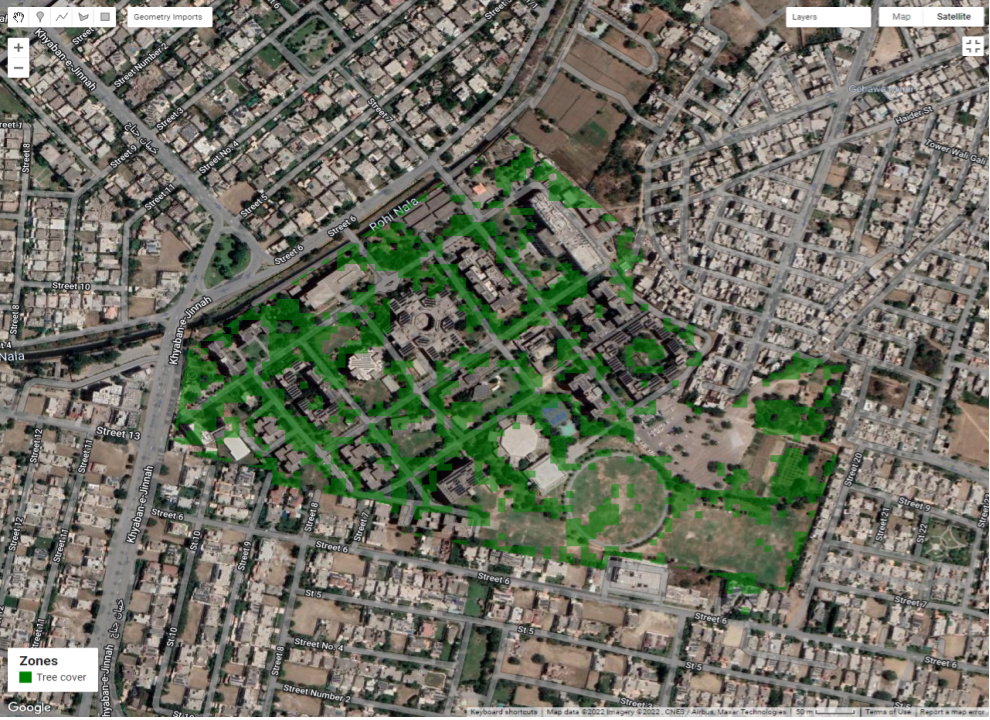

Green Space Classification
In this work we are classifying trees using a mixture of spectral indices.
- Vegetation Index (NDVI)
- Enhanced Vegetation Index (EVI),
- Normalized Difference Built-up Index (NDBI)
- Normalized Difference Moisture Index (NDMI)
- Enhanced Vegetation Index (EVI),
- Green Chlorophyll Index (GCI)
- Green Chlorophyll Index (GCI)
- Leaf Area Index (LAI) and Green Leaf Index (GLI) in our features set.
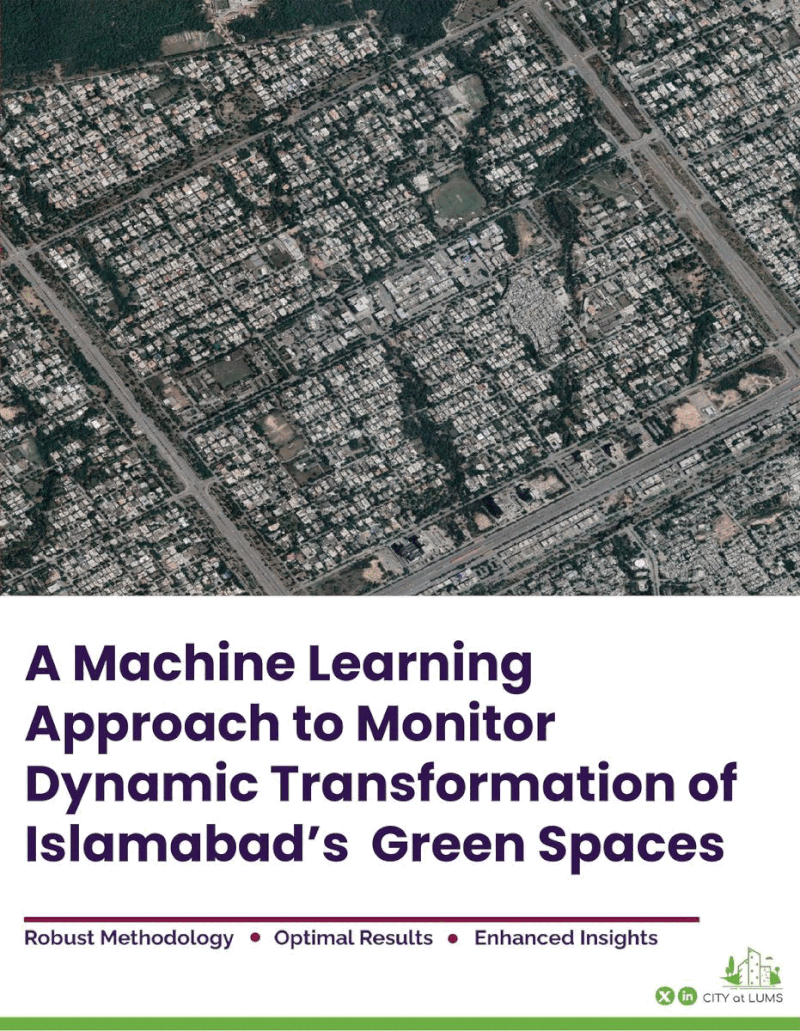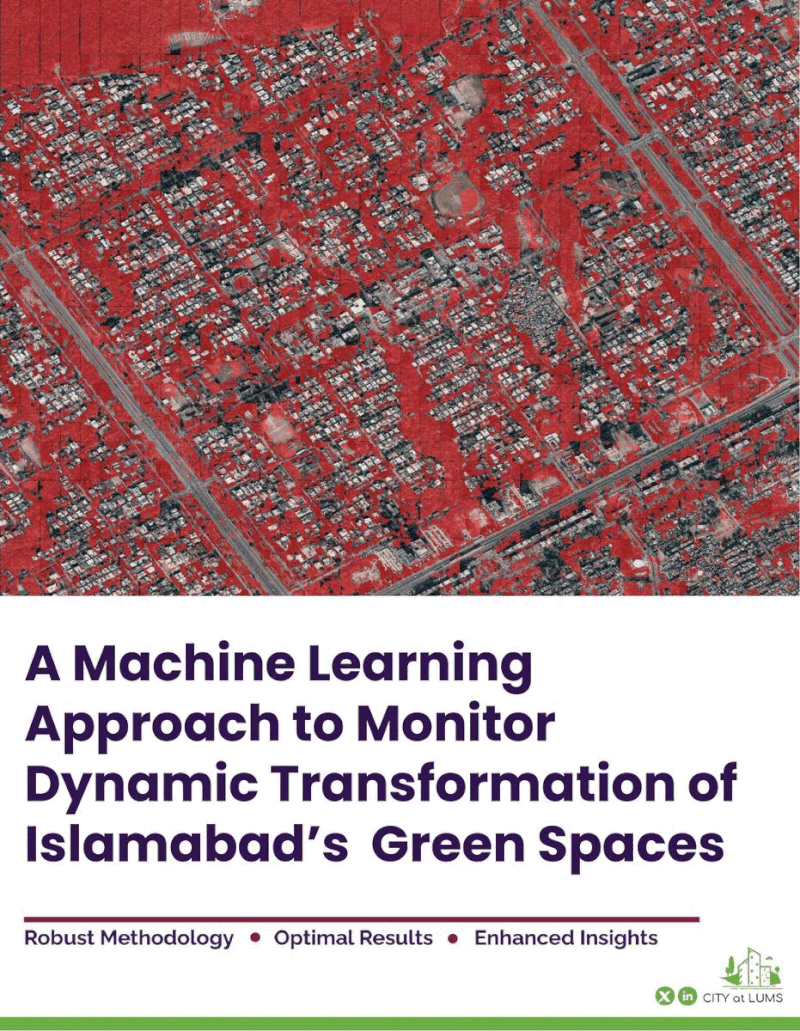
A machine learning model exploring the effects of rapid urbanization was developed to visualize the evolution of green spaces particularly over sector F7 in Islamabad, Pakistan's federal capital.
Through instance segmentation of pixels from high-resolution satellite imagery, the trained model visualized and calculated a significant decreasing trend in green spaces over the past 10 years. The maximum percentage decrease in the absolute area of greenspaces was recorded at 33%.
Given the current rate of urban sprawl, AI-Driven tools have great potential to contribute to sustainable urban development!
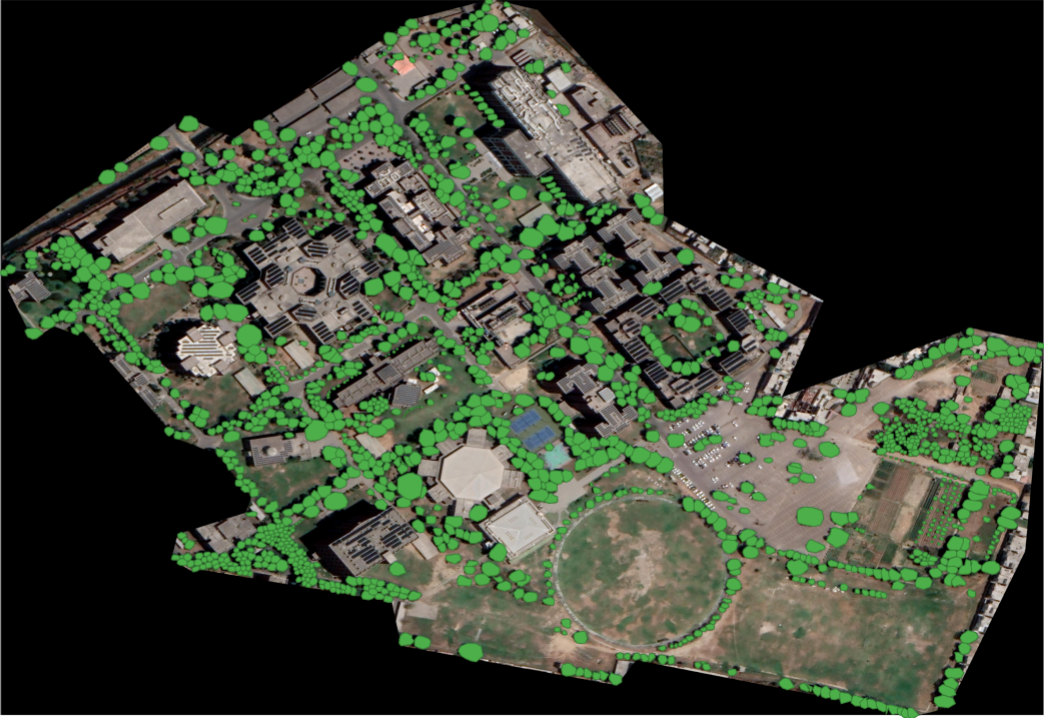
Tree Canopy Detection
CITY has developed novel tools to detect and assess tree canopy cover through AI detection and remote sensing. These tools can allow the following functions in ensuring sustainability of city design:
- Insights for cities about where to invest resources
- AI and aerial imagery detect tree canopy coverage
- Plan city projects.
- Track and Maintain Urban Forests

