
MOU Signing Trans Karachi
February 28, 2024
URBAN DICTIONARY
February 29, 2024
MOU Signing Trans Karachi
February 28, 2024
URBAN DICTIONARY
February 29, 2024
Points-Of-Interest (POIs) Datasets - The Possible Uses and Application
Points-of-Interest, or POI, are locations or features that are of particular interest or significance within a geographic area. These can include landmarks, businesses, public facilities like schools, hospitals, parks ATMs, and other points of interest that are often visited or referenced by people in the area.
POI Datasets:
POI datasets include, foremostly, the POI name, its category, geospatial coordinates (typically a longitude & latitude point, and less often a building footprint), business hours, contact information (e.g., website), and potentially — depending on the source — number of user reviews, average review rating, information about prices, photos, among others[1]. This data is often collected and maintained by government agencies, businesses, or other organizations as a way to better understand and serve the needs of the community.
Existing POI datasets at UTP and Possible Uses:
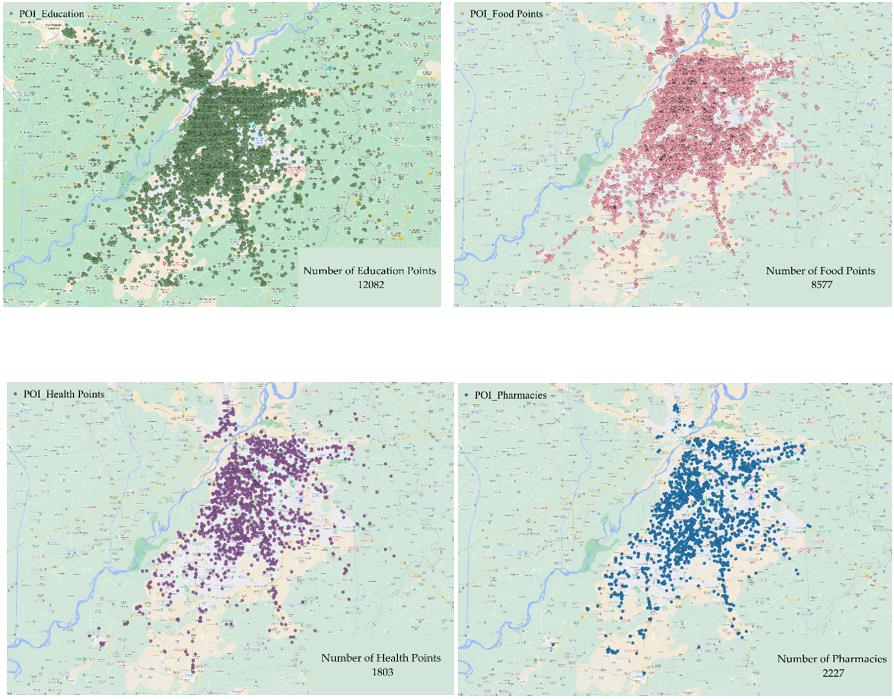
As a city with a diverse and vibrant population, Lahore faces a unique set of challenges and opportunities when it comes to providing access to essential amenities and services. By analyzing our comprehensive dataset of POIs such as schools, hospitals, restaurants, banks, and pharmacies (see images below), we can gain a deeper understanding of the distribution of these amenities across the city. This allows us to identify areas that may be underserved or in need of additional resources.
General uses of POI Dataset in various themes:
There are many different ways that POI data can be used, depending on the context and the needs of the organization or community. The following are a few common examples of the uses of POI data.
1 How can we use POIs in policy making?
POI data can be used by policymakers to make informed decisions about land use, infrastructure development, and other policy issues. For example, data on the locations and types of businesses in an area may be used to identify areas of economic growth or decline, and to make decisions about how to support local businesses. POI data can also be useful for government agencies in a variety of ways. Data on the locations of public facilities such as schools and hospitals can be used to identify areas where these facilities are needed, and to plan for future development.
- Education: Analyzing POI data can reveal patterns of educational attainment and access within a community to discover areas that may benefit from additional resources or support. For example, data on the locations of schools and other educational institutions can be used to identify areas where access to education is limited, and to develop plans for addressing these needs.
- Health: POI data can be used to identify patterns of health and wellness within a community, and to identify areas in need of additional resources or support. Data on the locations of healthcare facilities, such as hospitals and clinics, can be analyzed to identify areas where access to healthcare may be limited, and to develop plans for providing additional assistance as necessary.
- Disaster Response: POI data can also be valuable in the event of a natural disaster or other emergencies; it can help identify the locations of critical infrastructure, evacuation routes, and other resources that may be needed to respond to the disaster.
2 How can we use POIs to enhance urban development?
- Zoning and Land Use: POI data can be used to inform land use and zoning decisions, helping policymakers to identify areas that may be suitable for different types of development. For example, data on the locations of businesses, schools, and other points of interest could be used to identify areas where commercial development may be appropriate, or to identify areas that may be suitable for residential development.
- Gentrification: POI data can also be used to identify patterns of gentrification within a community, and to identify areas where these trends may be occurring. For example, data on the locations of new businesses or housing developments in an area may be used to identify areas where gentrification is occurring, and to plan for ways to address any negative impacts that may result.
3 How to use POIs to increase public safety by police?
POI data can be used by law enforcement agencies to identify areas of crime or other public safety concerns and to allocate resources appropriately.
- Emergency Response: POI data can be critical for emergency response and preparedness efforts, as it can help identify the locations of critical infrastructure or other resources that may be needed in the event of an emergency. For example, data on the locations of hospitals, fire stations, and other emergency response facilities can be used to identify where is the nearest hospital or rescue facility for improved response times.
- Public Safety: POI data can be used to inform the deployment of public safety resources, such as police patrols or emergency response facilities. For example, data on the locations of high-crime areas or areas with a high risk of natural disasters could be used to identify areas where additional resources may be needed to improve public safety.
4 How to use POIs to enhance urban mobility and tourism?
- Transportation Planning: POI data could be used to identify areas with high concentrations of businesses, schools, hospitals, and other destinations that are commonly visited by residents and visitors. This information could be used to determine the most efficient routes and schedules for buses, trains, and other public transportation services. Moreover, data on the locations of public transportation hubs, bike lanes, and other transportation infrastructure could be used to identify areas where additional resources or infrastructure may be needed, or to identify areas where these resources are being underutilized.
- Tourism: POI data can be especially valuable for tourism-related organizations and businesses, as it can help identify popular attractions and points of interest for visitors. For example, data on the locations of hotels, restaurants, and other tourist-oriented businesses can be used to create maps or itineraries for visitors, or to identify areas that may be underserved by these types of businesses.
5 How to use POIs to improve environment?
- Environmental Management: POI data can be used to identify and manage important natural or cultural resources within a community. For example, data on the locations of wetlands, conservation areas, or other ecologically significant areas can be used to protect and manage these resources, or to identify areas where extra caution needs to be practiced.
- Solid Waste Management: POI data can be used to inform the planning and operations of solid waste management systems. For example, data on the locations of businesses, residential areas, and other points of interest could be used to identify areas where additional waste collection or recycling facilities may be needed, or to identify areas where these resources are being underutilized.
- Air Quality: POI data can also be used to identify areas where air quality may be a concern, and to inform policies and initiatives aimed at improving air quality. For example, data on the locations of industrial or transportation-related sources of air pollution could be used to identify areas where additional monitoring or controls may be needed, or to identify areas where air quality may be a concern for public health.
6 Service Coverage and Resident Access to Amenities:
By combining this POI data with information on the road and transit networks in Lahore, we can also examine the transportation landscape in different areas and assess whether access to amenities is a barrier for certain populations. For example, are there areas where residents must travel long distances to access a school, hospital, or pharmacy? By answering these kinds of questions, we can identify opportunities to improve transportation infrastructure or service facilities and increase access to essential services.
In addition to examining access to amenities, we can also use our data to assess the availability of leisure and health facilities for the population of Lahore. By analyzing the average share of built-up areas and access to green spaces, we can determine whether the city is providing adequate opportunities for physical activity, social interaction, and mental relaxation. The World Health Organization (WHO) recommends that people live within a 500-meter (about 0.3 mile) walking distance of a park or green space. We can use this recommendation to guide our policy recommendations for increasing green spaces in underserved areas, possibly low-income areas and population-dense neighborhoods.
7 Financial Inclusion and Socioeconomic Characteristics of a Neighborhood:
By examining the distribution of banks in Lahore, policymakers can gain insight into the socio-economic characteristics of different areas within the city. Studies have shown that banks tend to be located in neighborhoods with higher income levels. Therefore, the presence or absence of financial institutions can be used as a proxy for understanding income and wealth distribution across different neighborhoods in Lahore.
Moreover, policymakers could also consider collecting and mapping data on income levels across neighborhoods, in addition to the locations of banks in Lahore. They could then use this data to create maps or visualizations showing the distribution of banks and socioeconomic characteristics across the city. Additionally, policymakers could consider conducting surveys or interviews with residents in different neighborhoods to gather more in-depth information about the availability and accessibility of financial services in different areas of Lahore. Overall, a more comprehensive understanding of the distribution of banks in Lahore and its relationship to income and wealth distribution can help policymakers design targeted policies and interventions to promote financial inclusion and improve economic outcomes for all residents.
Overall, our data provides a valuable resource for policymakers and government officials, seeking to make informed, evidence-based decisions about the distribution and availability of amenities and services in Lahore. By making the most use of this data, city managers can better understand the needs and interests of their constituents, and work to meet these needs in a more effective and efficient manner.

